
The command above will also install all the dependencies required for building Python modules. Use the following command to install pip for Python 3: sudo apt install python3-pip Start by updating the package list using the following command: sudo apt update
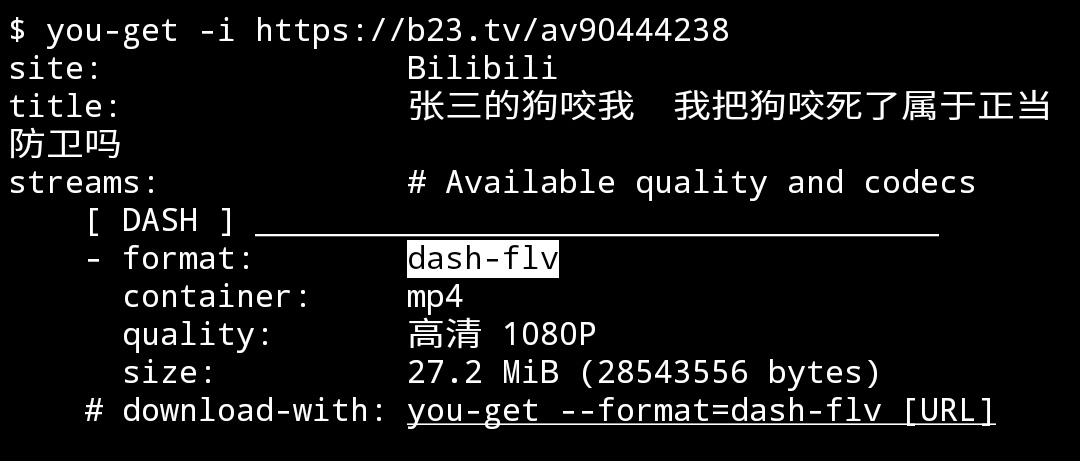
Complete the following steps to install pip ( pip3) for Python 3: Ubuntu 18.04 ships with Python 3, as the default Python installation. Prerequisites #īefore continuing with this tutorial, make sure you are logged in as a user with sudo privileges We will also walk you through the basics of installing and managing Python packages with pip. In this tutorial, we will show you how to install Python Pip on Ubuntu 18.04 using the apt Pip is not installed by default on Ubuntu 18.04, but the installation is pretty straightforward. The 'terminated' event is emitted when FFmpeg is terminated by calling FFmpeg.terminate().Pip is a package management system that simplifies installation and management of software packages written in Python such as those found in the Python Package Index (PyPI). The 'completed' event is emitted when FFmpeg is successfully exited. The 'progress' event is emitted when FFmpeg reports progress. progress: a namedtuple with frame, fps, size, time, bitrate, speed fields.The 'stderr' event is emitted when FFmpeg writes a line to stderr. The 'start' event is emitted just before FFmpeg is executed. arguments: a sequence of arguments to execute FFmpeg.Gracefully terminates the running FFmpeg process. execute()Įxecutes FFmpeg using specified options and files. An arbitrary number of output files can be specified by calling this method multiple times. An arbitrary number of input files can be specified by calling this method multiple times. Specifies a global option -key or -key value input(url, options=None, **kwargs) executable: the path to the ffmpeg executable.execute ()) API FFmpeg init(executable='ffmpeg') on ( 'error' ) def on_error ( code ): print ( 'Error:', code ) asyncio. on ( 'terminated' ) def on_terminated (): print ( 'Terminated' ). on ( 'completed' ) def on_completed (): print ( 'Completed' ). on ( 'progress' ) def time_to_terminate ( progress ): # Gracefully terminate when more than 200 frames are processed if progress. on ( 'progress' ) def on_progress ( progress ): print ( progress ). on ( 'stderr' ) def on_stderr ( line ): print ( 'stderr:', line ). on ( 'start' ) def on_start ( arguments ): print ( 'Arguments:', arguments ). output ( 'output.ts', # Use a dictionary when an option name contains special characters, f = 'mpegts', ). input ( 'rtsp:///cam', # Specify file options using kwargs rtsp_transport = 'tcp', rtsp_flags = 'prefer_tcp', ).
Usage import asyncio from ffmpeg import FFmpeg ffmpeg = FFmpeg (). A python interface for FFmpeg using asyncio Requirements


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
